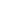
Parson Russell Terrier
The Parson Russell Terrier is the show dog version of the Jack Russell and Russell Terrier. These feisty and energetic pups make high-spirited, affectionate companions.
Interested in discovering if your dog is a Parson Russell Terrier?
Check out Wisdom Panel's DNA tests.

Parson Russell Terrier Traits
General Appearance
Parson Russell Terriers have square bodies and narrow chests—along with a smart and scruffy look.
Coat and Colouring
White with brown, black, tan, cream, or tricolor markings, the Parson Russell Terrier's double coat may be a combination of smooth and rough (wiry). This mixture of textures gives the coat a broken appearance.
Distinctive Physical Traits
Square and balanced, the Parson Russell Terrier has a slender build and an outgoing and animated step.
Parson Russell Terrier Temperament
Known worldwide for being an active and confident breed, the Parson Russell Terrier has a fearless and happy disposition. These dogs make loving companions and always want to be a part of the family fun.
Keep in mind that, if restricted to a small area and left alone, the Parson Russell will take matters into its own paws. This may mean digging up the yard or crawling under the fence to explore—or anything in between.
Parson Russell Terriers may chase wildlife or other dogs. And they're often challenging to disengage from an activity that has their attention.


Parson Russell Terrier History
The Parson Russell descends from early, white-bodied working terriers.
Reverend John Russell developed the breed to hunt fox during the 1800s. The small-bodied dogs helped drive foxes from their lairs, giving the hunters easy access.
The Kennel Club of the United Kingdom first recognized Parson Russell Terriers in 1990. And the breed received American Kennel Club recognition in 1997.
Parson Russell Terrier Care
Nutrition
Parson Russell Terriers need to eat high-quality food that's appropriate for their life stage (e.g., puppy, adult, senior). To keep them at a healthy weight, monitor food portions carefully. And be sure to take treats into account when tracking their daily calorie intake. As a guideline, treats should make up no more than 10% of a dog's calories.
Grooming
The Parson Russell Terrier can have one of two coat types: smooth or broken. Both require regular brushing.
Use a thick brush or hound glove on the smooth part of the coat and a pin or slicker brush—to lift loose hair and debris—on the rough parts. The rough coat of a Parson Russell Terrier will need plucking or clipping to avoid matting of the longer hairs.
Monthly bathing and nail trims are adequate for this breed. But you should check and clean the ears of your Parson Russell Terrier weekly to avoid wax buildup and the accumulation of debris.
Exercise
Parson Russell Terriers love to run—whether in an open field, woodsy trail, or neighborhood park. This high-energy breed enjoys fetching, agility, flyball, and frisbee. Parson Russell Terriers also have the keen sense of smell necessary to participate in earthdog trials.
This breed has a strong prey drive, so a leash (or fenced-in yard) is mandatory. The Parson Russell Terrier won't be satisfied sitting alone in a secluded spot for any length of time.
Training
Eager to learn, and well-suited for reward-based training, the Parson Russell Terrier needs consistent and strong guidance. This breed tends to get bored easily, so aim to keep training fun and interesting.
And remember, early socialization helps puppies of all breeds develop into well-mannered adult dogs.

Parson Russell Terrier Genetic Health Conditions
-
Amelogenesis Imperfecta (Discovered in the Parson Russell Terrier)
Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI), also known as enamel hypoplasia, is a disorder where the hard enamel covering of the teeth is thin, roughened and discolored.
-
Chondrodystrophy (CDDY) and Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD) Risk
Chondrodystrophy (CDDY) is a skeletal disorder characterized by shortened limbs and abnormal early degeneration of the spinal discs, or intervertebral disc disease (IVDD), which predisposes to disc herniation.
-
Hyperuricosuria
Hyperuricosuria (HUU) is a condition that predisposes affected dogs to the formation of urinary stones, such as kidney or bladder stones.
-
Juvenile Encephalopathy (Discovered in the Parson Russell Terrier)
Juvenile encephalopathy is a brain disorder causing epileptic seizures and progressive brain damage.
-
Primary Lens Luxation
Primary Lens Luxation (PLL) is a condition that can cause the lens of the eye to become loose and eventually displace. The disorder is caused by degeneration of the fibers that hold the lens in place.
-
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (Discovered in Russell Terriers)
Autosomal Recessive Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (ARSCID) is a severe immunodeficiency disorder discovered in Jack Russell Terriers, that leaves affected dogs prone to infection.
-
Spinocerebellar Ataxia (Late-Onset Ataxia)
Spinocerebellar Ataxia also known as Late Onset Ataxia (LOA) is a disease of the nervous system characterized by uncoordinated movements and impaired balance.
-
Spinocerebellar Ataxia with Myokymia and/or Seizures
Spinocerebellar Ataxia with Myokymia and/or Seizures (SAMS) is a disease of the nervous system characterized by uncoordinated movements and impaired balance. This particular form may present with muscle twitching and seizures.
Knowing if your Parson Russell Terrier is a carrier or at-risk for these conditions can help you and your veterinarian plan for your pup's lifelong care. With Wisdom Panel™ Premium, you can get results for over 200 genetic health tests.
Breed Group
Terrier
The Terrier Group ancestors were bred to hunt and kill vermin. They are often characterized as feisty and energetic dogs whose sizes range from fairly small to much larger.
Resources
https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/parson-russell-terrier/
Reviewed 26 July 2020 by Laura Inman, DVM